AI Agents: A New Stage in the Evolution of User Experience
AI agents are autonomous software systems that perceive the environment, make decisions, and perform actions to achieve set goals without constant human oversight. In recent years, the development of AI agents has become one of the key trends in artificial intelligence, changing approaches to automation, business, and user experience.
Most modern AI agents are based on large language models such as GPT, Claude, Gemini, and others. LLMs make it possible to understand complex text queries and conduct dialogue in natural language. However, with the emergence of agency, LLMs go beyond the familiar chat window: they can now not only answer questions but also initiate actions in the external world — book tickets, launch processes, manage applications, integrate with services, and automate complex business processes.
Evolution of User Experience
Before Internet Applications
Previously, solving everyday tasks required physical presence and manual actions. For example, to buy a train or plane ticket, you had to go to the ticket office, stand in line, explain travel details to an employee, and pay in cash.
With the Advent of Internet Applications
Internet services radically simplified access to services. Users could go to an airline or aggregator website, choose a route, specify a date, compare prices, fill out an online form with passport details, and pay for a ticket with a card. However, this required navigating the interface, switching between pages, and monitoring data accuracy.
With the Arrival of AI Agents
AI agents take the next step: now it's enough to describe your task in natural language, and the agent will independently perform all necessary actions. For example, to buy a plane ticket, it's sufficient to say:
"Find me a direct flight from Almaty to Dushanbe for the nearest Friday, with a morning departure and a price not exceeding 50,000 tenge. Complete the purchase in my name and send the boarding pass to my email."
The AI agent independently analyzes schedules, compares prices on different platforms, selects the optimal option, books the ticket, and sends all information to the user. If needed, it will clarify details or offer alternatives.
This approach saves time, eliminates the need to navigate interfaces, minimizes errors, and makes the process maximally convenient and personalized.
Levels of Autonomy for AI Agents
Below is an example of AI agent autonomy to represent the levels at which we will interact with them.
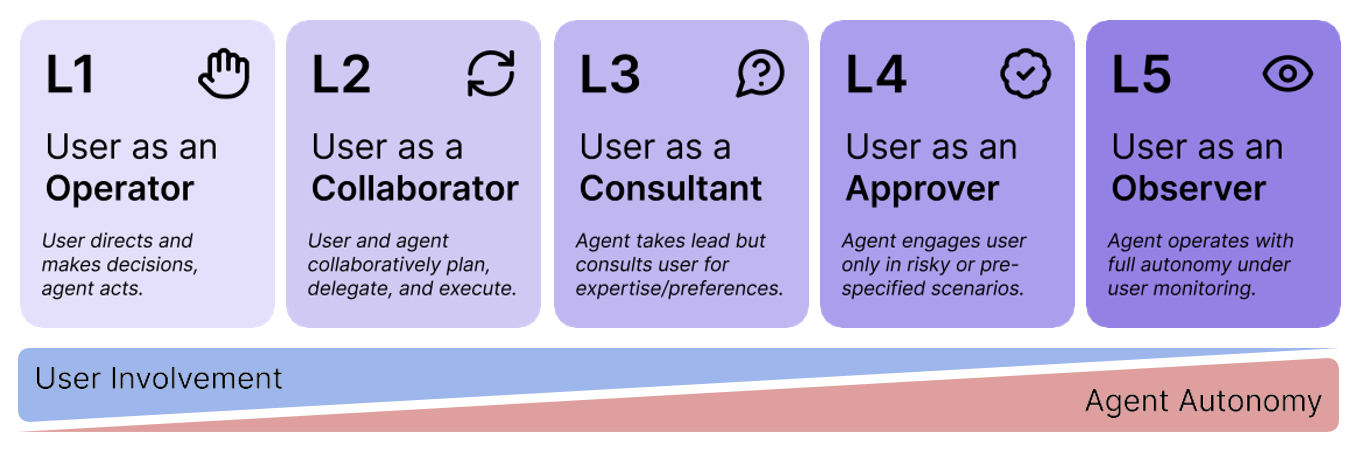
Source:Levels of Autonomy for AI Agents
Today, levels L1 and L2 are actively developing. For example, coding assistants like Github Copilot, Gemini Code Assist, and Claude Code are at level L1, while more autonomous agents for code creation like Lovable and Bolt are close to level 2.
How the Internet Will Change with AI Agent Development
The development of AI agents is just beginning. With the strengthening of LLMs and technology implementation in industries, agents will reach increasingly higher levels of autonomy and capabilities.
- •Interface becomes invisible: more and more tasks will be solved through dialogue or a short request, without the need to navigate website interfaces
- •Service integration: agents will be able to combine actions in different systems — booking tickets, hotels, and taxis simultaneously
- •Barrier to entry decreases: no need to learn to use dozens of websites — just being able to formulate your tasks is enough
- •New automation scenarios: agents will be able to perform complex tasks that were previously too difficult for manual work through web interfaces
- •Deep personalization: agents will consider your preferences, history, and context, offering solutions that are maximally suited to you
Forecasts and Challenges
Forecasts
- •Within three to five years, AI agents will become the standard for automating not only routine but also creative tasks
- •The number of multi-agent systems will grow, where virtual employees coordinate complex processes without human participation
- •New professions will emerge: agent designers, agent system trainers, AI ethics auditors
Challenges
- •Ensuring transparency and explainability of agent decisions
- •Ethical questions: privacy, responsibility, fairness
- •Integration with legacy systems and staff training
- •The need to control autonomous decisions and prevent errors at early stages
Conclusion
AI agents are not just another turn in technological development, but a fundamental shift in how we interact with the digital world. They make technology more accessible, natural, and effective for users of any skill level. For business, this is an opportunity not only to automate routine processes but also to create new products, improve customer experience, and open additional sources of growth.
However, implementing AI agents requires a conscious approach: it's important to consider issues of transparency, security, ethics, and control over autonomous decisions. Market leaders who can build a balance between innovation and responsibility will gain significant competitive advantages in the coming years.
We are currently standing at the threshold of a new era, where AI agents become the connecting link between humans and digital ecosystems. The realization of their potential will determine not only business efficiency but also quality of life in general.
Sources
This article was originally published in Russian on The Tech.